Universal Media Storage

Scale-out Data Storage System
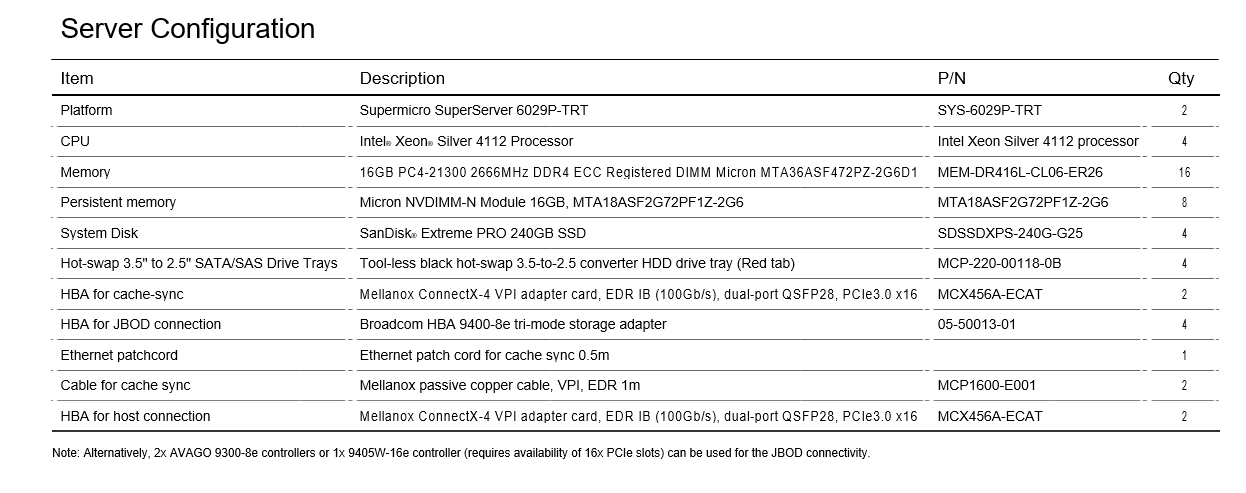
Storage servers: Supermicro SuperServer 6029P-TRT
Metadata servers: Supermicro SuperServer SSG-6028R-E1CR12L
JBOD: Ultrastar Data102 with HDDs and SSDs
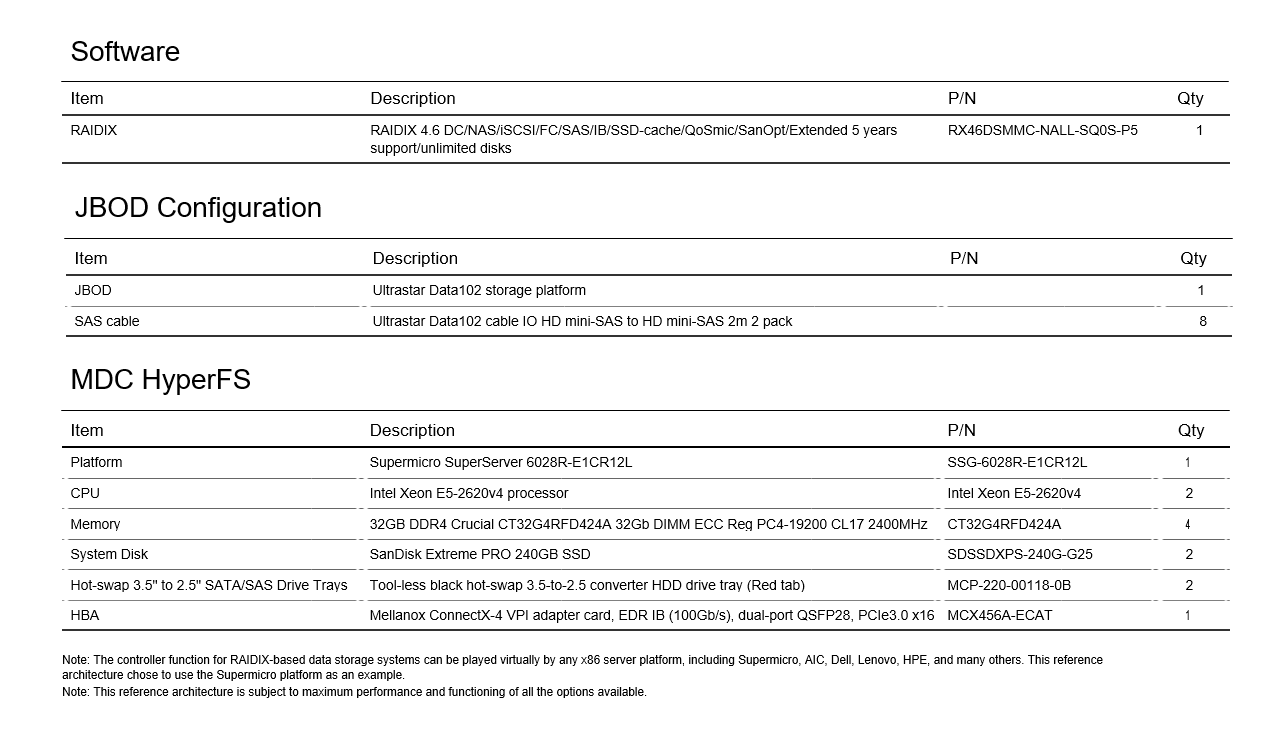
SW: RAIDIX 4.6
Storage servers: Supermicro SuperServer 6029P-TRT
Metadata servers: Supermicro SuperServer SSG-6028R-E1CR12L
JBOD: Ultrastar Data102 with HDDs and SSDs
SW: RAIDIX 4.6
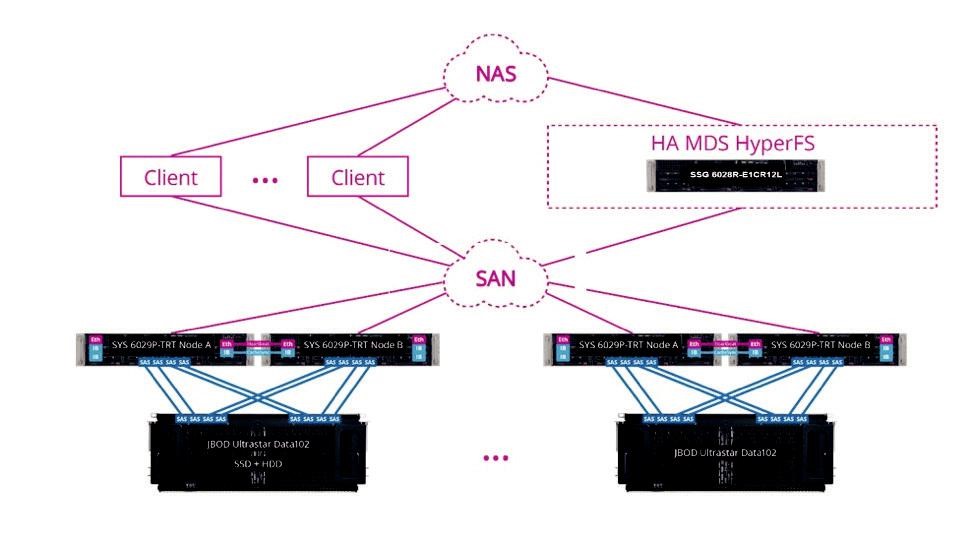
To create a scale-out system based on HyperFS, two types of servers are required — one for data storage and one for metadata storage.
- 1. The data storage controller function will be performed by the SuperMicro® SuperServer® 6029P-TRT
- 2. To store metadata, several SSDs are installed in the Ultrastar® Data102 storage platform. They are configured into a RAID configuration and access to the MDS is provided via a SAN.
It is possible to connect up to four Ultrastar Data102 storage platforms to one storage server in cascade. The RAIDIX software controller function runs on top of the storage nodes.
Overall, 5.5 PB1 of data is placed in one deep storage rack with one common namespace.
Target Applications:
- • HPC (Life Sciences: DNA and RNA sequencing, climate research)
- • Technical computing (CAS/CAM, Simulations)
- • Video Surveillance, up to 10,000 Full HD cams
- • Media & Entertainment (Content delivery and streaming, content archive, content management)
For purposes of server sizing, the PCIe bus is used to install backend and frontend controllers. Broadcom® 9400 8e controllers are used to connect the Ultrastar Data102 storage platform to the Supermicro servers. The synchronization channel slot is Infiniband, supported by Mellanox® ConnectX-4 VPI adapter card (PCIe3.0 x16) on each node.
The server is equipped with Micron® NVDIMM modules to protect the cache from power outage. Dirty cache segments will be synchronized via InfiniBand 100Gb.
The Ultrastar Data102 can be equipped with Ultrastar DC HC510, HC520, or HC530 (when available) SAS HDDs, providing a data repository of up to 1.4PB in a 4U storage rack. Minimum configuration is 60 drives, providing an upgrade path of up to 102 drives. Up to 24 SAS/ SATA SSDs can be installed in those drive slots to provide storage for the metadata.
---
Note: Each controller must have at least five x8 slots (without room for further scaling). Systems built for lower performance of 3-4 Gbps per node can be configured with only two slots.
Note: Ultrastar Data102 can also be switched out for Ultrastar Data60, if the depth of your rack is not sufficient to host the Ultrastar Data102 (Depth: 1047mm (41.25”) or Depth in Rack: 1197mm (47.13”) w/ CMA.
1One MB is equal to one million bytes, one GB is equal to one billion bytes, one TB equals 1,000GB (one trillion bytes), and one PB equals 1,000TB when referring to hard drive capacity. Accessible capacity will vary from the stated capacity due to formatting and partitioning of the hard drive, the computer’s operating system, and other factors.